What is Google Search Console?
Google Search Console (GSC) is a free tool that empowers site owners to track their organic search results, request page indexing, and much more.
Features of GSC include but are not limited to:
- Tracking organic search traffic
- Requesting indexing of pages
- Monitoring indexing and crawling
- Identifying and fixing bugs
- Reviewing internal and external links
- Tracking mobile usability issues (soon to be retired)
- Analyzing click-through rates (CTR) for queries
- Viewing top search queries leading to your site
- Understanding country-specific performance
What is Google Search Console Mainly Used For?
GSC is primarily used for the following:
| Overview of search performance | Finding the most linked-to pages | Sitemaps |
| Basic search console usage | Internal links | Mobile usability (soon to be retired) |
| Identifying your top pages | Core Web Vitals | Request indexing of updated pages |
| URL Inspection | Track average position in Google | Page experience overview |
» MORE: Google’s Local Guides Program: Everything You Need to Know
4 Ways Google Search Console Improves Website Design
1. User Experience
Google Search Console can improve your website’s user experience in the following ways:
See What Is Already Working
GSC shows which pages on your website are popular, which can help you optimize your underperforming pages. After all, once you know what works, the changes you make will be beneficial.
Identify Slow Pages
GSC helps identify pages that are slow to load, which is a critical UX factor.
Note that the speed report in GSC has been replaced with Core Web Vitals. GSC now shows you one of two indicators when your web pages aren’t loading quickly:
LCP issue: longer than 2.5s (This means your loading performance needs improvement.) ⚠️
LCP issue: longer than 4.0s (This means your loading performance is poor.) ❌
Manage Internal and External Links
GSC provides data on how pages are interlinked. Based on this information, your site’s navigation can be improved for a better UX.
2. Mobile Usability
Google Search Console has a “Mobile Usability” feature that shows which of your web pages are mobile-friendly.
This is one of GSC’s best features, although, unfortunately, it will soon be retired.
You can read more about why Google is retiring it here:
For those unfamiliar with mobile usability, it is a key factor in web design and Google SEO rankings. This is because over half of internet users access websites via mobile devices.
Need a mobile-friendly website? Learn more on our WordPress Web Design Services page.
3. On-page Content
GSC shows you the top queries on your website, which can inform your future on-page content efforts.
For more information on how to improve your rankings and traffic with Google Search Console, check out this video from Surfside PPC:
4. Internal & External Links
Google Search Console’s Links report details your website’s internal and external links, including top linked pages and linking text.
This feature is useful for website owners who want to improve their website navigation.
For instance:
If a page has a lot of internal links, it’s almost certainly a central component of your navigation, so this page should be easy to find and access. 🔎
While this sounds obvious, sometimes important pages and blog posts can get buried beneath other content by accident. The Links report helps in identifying such pages and more.
Learn more about Google Search Console’s Links report here: Links report
» ADDITIONAL: Google Trends: What Is Google Trends and How To Use It
Want to Use GSC? Here’s How…
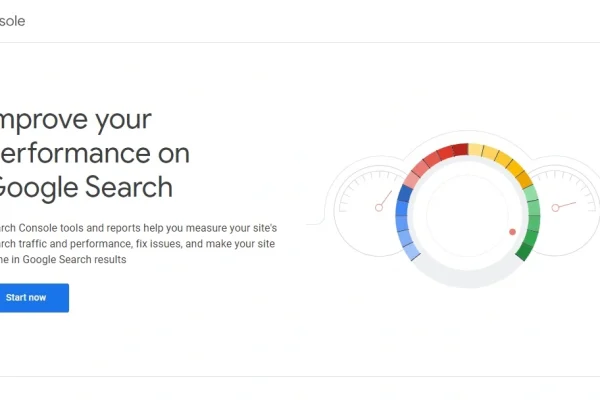
To use Google Search Console, visit the GSC About page and click the “Start now” button.
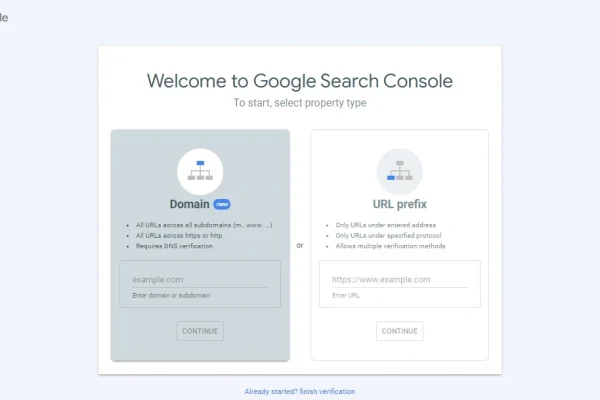
Once you click Start now, the next page will say, “Welcome to Google Search Console. To start, select property type.”
Click image to expand
Two Ways to Verify Your Site in Google Search Console
Google Search Console allows you to add and verify your website in two main ways: “Domain” and “URL prefix.”
Here’s a breakdown of what these mean.
Domain (method 1):
This method lets you view data for your entire website.
For instance, if your website is mysite1234.com, verifying the “Domain” would cover shop.mysite1234.com, blog.mysite1234.com, etc.
It would also cover protocols http://mysite1234.com and https://mysite1234.com.
URL prefix (method 2):
This method is more specific.
Say you verify https://www.mysite1234.com using the “URL prefix” method.
GSC will only show data for this URL, plus add-ons such as https://www.mysite1234.com/blog.
It won’t show data for a different setup like blog.mysite1234.com or a different protocol like http://mysite1234.com.
In short:
Domain = data for the entire website.
URL prefix = data for a specific part of the website.
Method 1: Domain Verification via DNS Record
Google Search Console allows you to verify your domain ownership via DNS record through Cloudflare.com or any DNS provider.
To learn more about this process, check out this helpful walkthrough video from Google Search Central:
Method 2: URL Prefix
Google Search Console offers five methods to verify your URL prefix.
- HTML file upload to your site
- HTML tag (add a meta tag to the home page)
- Google Analytics (verify through your Google Analytics account)
- Google Tag Manager (verify through your Google Tag Manager account)
- Domain name provider (associate a DNS record with Google)
Are You Ready to Get Started?
Connect with Sage Digital Agency for answers to your questions, pricing information, and more!
» FURTHER READING: 25 Interesting Things You Can Do With Google Lens